Balanced Diet And Plate Portioning
Balance diet and plate portioning is the vital topic to understand. A balanced diet is one in which macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, and fat) are consumed in adequate quantities to meet the body’s requirements without excess intake while also providing sufficient micronutrients and hydration to support the body.
The main source of energy in the diet is carbohydrates, which are most prevalent in grains, fruits, legumes, and vegetables.
Dietary proteins provide a source of energy as well as amino acids (both essential and non-essential). Animal (meat, dairy, fish, and eggs) and plant (legumes, soy products, grains, nuts, and seeds) source both provide dietary proteins; however, the animal source is thought to be a richer supply due to the variety of amino acids, high digestibility, and increased bioavailability.
In addition to serving as a source of energy, fat also functions as a component of cellular membranes.
Fats are divided into four categories:
- Polyunsaturated fats.
- Monounsaturated fat.
- Saturated fat.
- Trans fat.
Unsaturated dietary fats are linked to lower mortality and cardiovascular risks, but trans fats and, to a lesser extent, saturated dietary fats are linked to adverse health effects, including higher mortality risk.
Omega-3 and omega-6 families of polyunsaturated fatty acids are referred to be essential fatty acids because they are needed for healthy growth and reproduction but cannot be synthesized by the body and must therefore be received from food. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), two omega-3 fatty acids have been extensively researched for their potential health benefits.
Evidence suggests that these fatty acids may help maintain muscle mass, prevent cognitive decline, reduce inflammation, and improve systemic insulin resistance.
Micronutrients are essential for healthy growth, metabolism, physiologic functioning, and cellular integrity even though they are only needed in trace amounts in comparison to macronutrients. As most people in the modern world are relying on processed food, a higher amount of micronutrient deficiency is seen.
Water makes up the bulk of lean body mass and total body weight, making it the primary constituent of the human body. In addition to hydrating the body, water also transports micronutrients like electrolytes and trace minerals. Up to 20% of the daily required intake of calcium and magnesium may be obtained through drinking water.
The daily recommended intake of water is mentioned in the table below:

How to portion your plate?
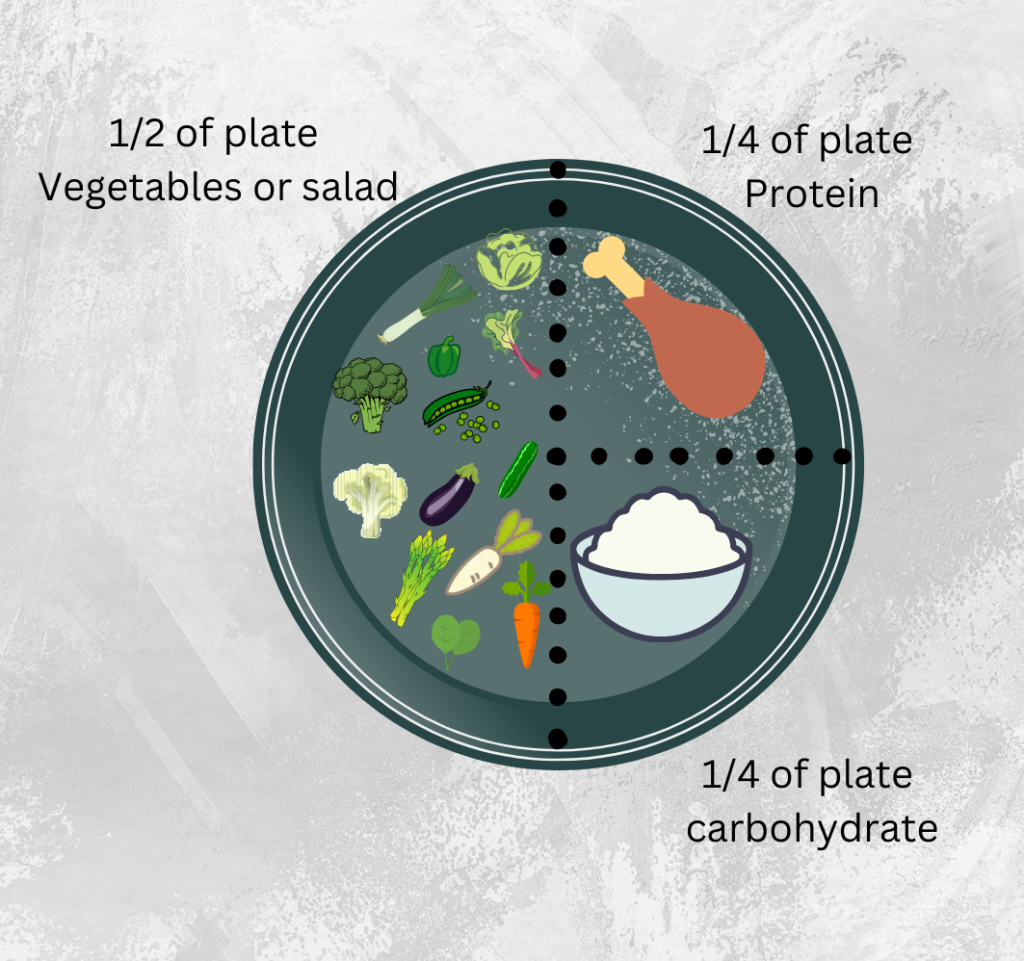
Half (50%) of our plate should be filled with vegetables as they are rich in antioxidants, micronutrients, and macronutrients mandatory for the smooth and healthy functioning of our body. Similarly, one-fourth (25%) of the plate should be filled with complex carbohydrates and the remaining one-fourth (25%) should contain protein. You should try to eat at least five servings of vegetables and two serves of fruit per day. Likely, you should try to aim for 4-6 serves of grains per day.
What is the suitable portion of macronutrients for you?

For a complex carbohydrate, your one cupped hand is a serving size. The size of your thumb is the reference for one serving of fats and oils for you. Similarly, one fist size is the recommended portion for vegetables. It Is suggested to have at least two servings of vegetables per meal, covering half part of your plate. The size of your palm is the reference for the portion of protein.
References
Australian Government. (2018). Why I should eat: wholegrains. Qld.gov.au. https://www.health.qld.gov.au/news-events/news/why-you-should-eat-wholegrains-wholemeal-cereal-serves
Cena, H., & Calder, P. C. (2020). Defining a healthy diet: Evidence for the role of contemporary dietary patterns in health and disease. Nutrients, 12(2), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12020334
Eat for Health. (2012, October 29). Serve Sizes | Eat for Health. Eatforhealth.gov.au. https://www.eatforhealth.gov.au/food-essentials/how-much-do-we-need-each-day/serve-sizes
Marcin, A. (2018, November 2). How Much Water You Need to Drink. Healthline; Healthline Media. https://www.healthline.com/health/how-much-water-should-I-drink








Excellent. This give the knowledge about portioning and diet and simple and easy way. And also tha water intake i might be lack on it but will make sure to have required ml of water daily.
Thank you